Unveiling The Truth: Are Coffee Grounds Green Or Brown Compost? Discover The Secrets And Take Action Now!
Are Coffee Grounds Green or Brown Compost?
Introduction
Dear Coffee Enthusiast,
1 Picture Gallery: Unveiling The Truth: Are Coffee Grounds Green Or Brown Compost? Discover The Secrets And Take Action Now!
Welcome to this informative article where we will delve into the world of coffee grounds composting. If you’re a coffee lover who is passionate about sustainability and gardening, you must have wondered about the color of coffee grounds and how they contribute to composting. In this article, we will explore whether coffee grounds are considered green or brown compost, providing you with all the necessary information you need to know. So, let’s dive in!
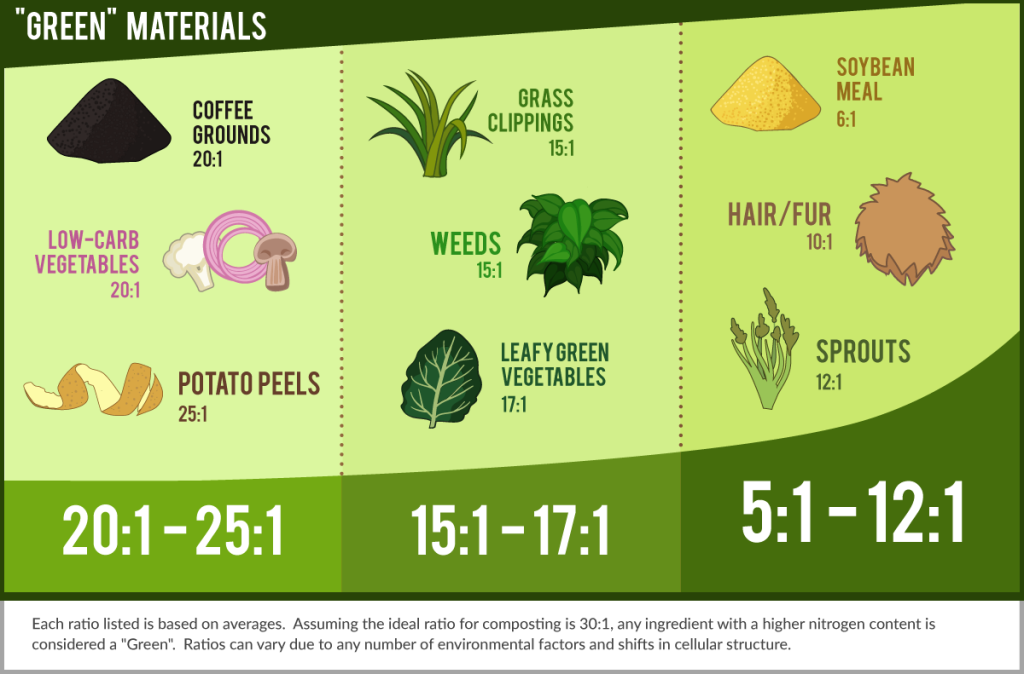
Image Source: petpooskiddoo.com
Before we begin, let’s first understand the basics of composting. Composting is the process of decomposing organic materials such as kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials into nutrient-rich soil. The final product, known as compost, can be used to enrich garden soil, reduce waste, and promote a healthier environment.
In composting, materials are categorized into two main groups: green and brown. Green materials are rich in nitrogen and moisture, while brown materials are high in carbon and provide structure to the compost. The balance between these two types of materials is crucial for a successful composting process.
What are Coffee Grounds?
Coffee grounds are the residue left behind after brewing coffee. They are dark and granular in texture, with a distinct aroma. Many coffee enthusiasts discard these grounds without realizing their potential as a valuable resource for composting.
Contrary to popular belief, coffee grounds are considered green compost instead of brown. This is due to their high nitrogen content, which contributes to the decomposition process and provides essential nutrients to the compost. However, it’s important to note that coffee grounds should be balanced with brown materials for optimal composting results.
So, why are coffee grounds classified as green compost? Let’s explore the reasons behind this classification.
Why are Coffee Grounds Considered Green Compost?
1. Nitrogen-rich: Coffee grounds contain high levels of nitrogen, which is a key component for the growth of microorganisms responsible for breaking down organic matter.
2. Moisture retention: Coffee grounds have excellent moisture retention properties, keeping the compost pile adequately moist and ensuring optimal conditions for decomposition.
3. Stimulate microbial activity: The microorganisms present in coffee grounds aid in the decomposition process by breaking down organic matter into simpler compounds.
4. Speed up decomposition: Due to their high nitrogen content, coffee grounds accelerate the decomposition process, resulting in faster compost production.
5. Nutrient contribution: Coffee grounds add valuable nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus to the compost, enriching the soil and promoting healthy plant growth.
6. pH balance: Coffee grounds are slightly acidic, which helps balance the pH level of the compost, creating a favorable environment for the breakdown of organic matter.
7. Waste reduction: Utilizing coffee grounds for composting not only reduces waste but also prevents them from ending up in landfills, where they contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Coffee Grounds Composting
Advantages
1. Natural fertilizer: Coffee grounds provide essential nutrients to plants, acting as a natural fertilizer and promoting healthy growth.
2. Organic waste management: Composting coffee grounds reduces organic waste and promotes a more sustainable way of managing kitchen scraps.
3. Soil enrichment: Adding coffee grounds to compost improves soil structure, moisture retention, and nutrient content, creating a fertile environment for plants.
4. Cost-effective: Composting coffee grounds is a cost-effective solution for gardeners, as it eliminates the need to purchase commercial fertilizers.
5. Environmental impact: By diverting coffee grounds from landfills, composting reduces greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to a greener planet.
Disadvantages
1. Imbalance in compost: Using coffee grounds excessively without balancing them with brown materials can create an imbalance in the compost, leading to odor issues and slow decomposition.
2. Attract pests: Coffee grounds may attract pests such as fruit flies and ants if not properly managed or if used excessively.
3. pH alteration: While slightly acidic coffee grounds can help balance the pH of the compost, excessive amounts can alter the pH, affecting the growth of certain plants.
4. Limited nitrogen source: While coffee grounds contain nitrogen, they should not be relied upon as the sole source of nitrogen in a compost pile. Adding other nitrogen-rich materials is necessary for a healthy composting process.
5. Not suitable for all plants: Some plants may be sensitive to coffee grounds due to their acidity or caffeine content. It’s important to know which plants benefit from coffee grounds and which do not.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can coffee grounds be composted with other kitchen scraps?
Yes, coffee grounds can be composted with other kitchen scraps such as fruit and vegetable peels, eggshells, and tea bags. Just make sure to maintain a proper balance between green and brown materials.
2. How should I store coffee grounds before adding them to the compost?
It’s best to store coffee grounds in an airtight container in a cool, dry place until you’re ready to add them to the compost. This prevents the grounds from drying out or becoming moldy.
3. Can I use coffee filters in composting?
Yes, coffee filters made from unbleached paper can be composted along with the coffee grounds. However, avoid using filters made from synthetic materials or those that have been bleached.
4. Are there any plants that don’t benefit from coffee grounds?
Some plants, such as blueberries, prefer acidic soil and benefit from coffee grounds. However, plants like tomatoes and peppers are more sensitive to acidity and may not thrive with excessive coffee grounds.
5. How long does it take for coffee grounds to decompose in compost?
Coffee grounds generally decompose within a few months in a well-maintained compost pile. However, the decomposition time can vary depending on factors such as temperature, moisture levels, and the overall composition of the compost pile.
Conclusion
In conclusion, coffee grounds are considered green compost due to their high nitrogen content and ability to contribute to the decomposition process. When used in moderation and balanced with brown materials, coffee grounds can be a valuable resource for composting, providing essential nutrients to the soil and promoting sustainable waste management. By composting coffee grounds, you can play a role in reducing waste, enriching soil, and creating a greener environment. So, the next time you make a cup of coffee, remember to save those grounds for your compost pile!
Final Remarks
Composting coffee grounds is an excellent way to reduce waste and create nutrient-rich soil for your plants. However, it’s important to note that every garden and compost pile is unique. Factors such as the composition of your compost, the plants you’re growing, and your local climate can all affect the success of coffee grounds composting. It’s always advisable to observe your compost pile, monitor its progress, and make adjustments as needed. Happy composting!
This post topic: Green Coffee



